Harish Projects
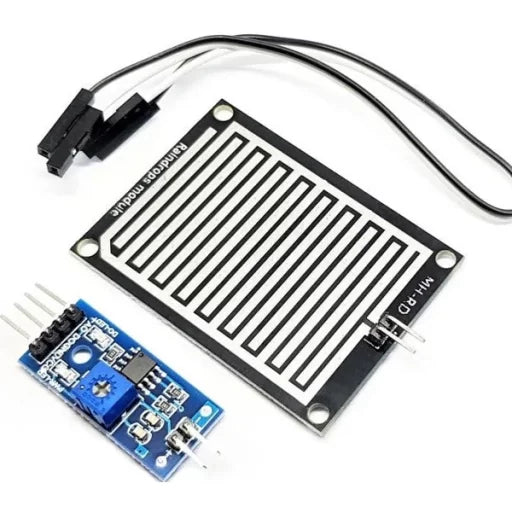
Raindrop Sensor Module | Water Drop Detection Sensor | Rain & Water Level Sensor for Arduino, IoT & DIY Projects
Raindrop Sensor Module | Water Drop Detection Sensor | Rain & Water Level Sensor for Arduino, IoT & DIY Projects
Couldn't load pickup availability
Share
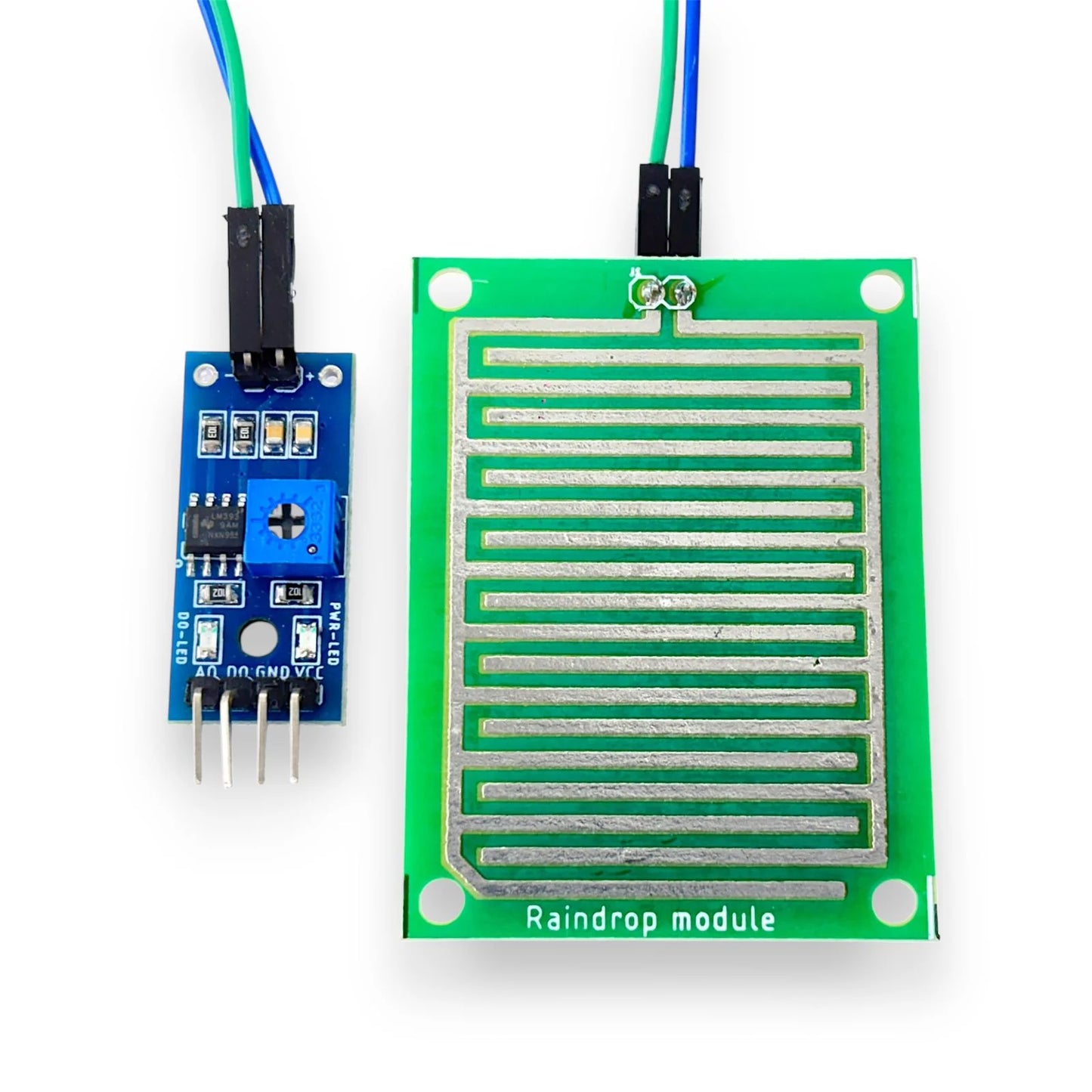
Technical Specifications
- Product Type: Raindrop / Water Drop Sensor Module
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V – 5V DC
- Detection Principle: Resistance change due to water droplets
- Output Type: Analog & Digital
- Comparator IC: LM393
- Sensitivity Adjustment: Onboard potentiometer
- Indicator LEDs: Power LED and Output LED
- Sensor Plate Material: Nickel-plated copper
- Interface Compatibility: Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP8266, ESP32, IoT boards
- Applications: Rain detection, water leakage detection
Product Description
The Raindrop Sensor / Water Drop Sensor Module is a simple and effective solution for detecting rain or water droplets. It works by sensing changes in electrical resistance when water falls on the sensor plate, making it ideal for rain detection and water leakage monitoring.
Operating on 3.3V to 5V DC, this module is fully compatible with Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP8266, ESP32, and other IoT platforms. It provides both analog and digital outputs, allowing users to measure rain intensity or trigger alarms and automation systems. The onboard LM393 comparator and adjustable sensitivity potentiometer enable precise control over detection levels.
Perfect for automatic rain sensing systems, weather monitoring projects, smart irrigation, water leakage alarms, and educational electronics experiments, this raindrop sensor module is widely used by students, hobbyists, and developers.

Good


