Harish Projects
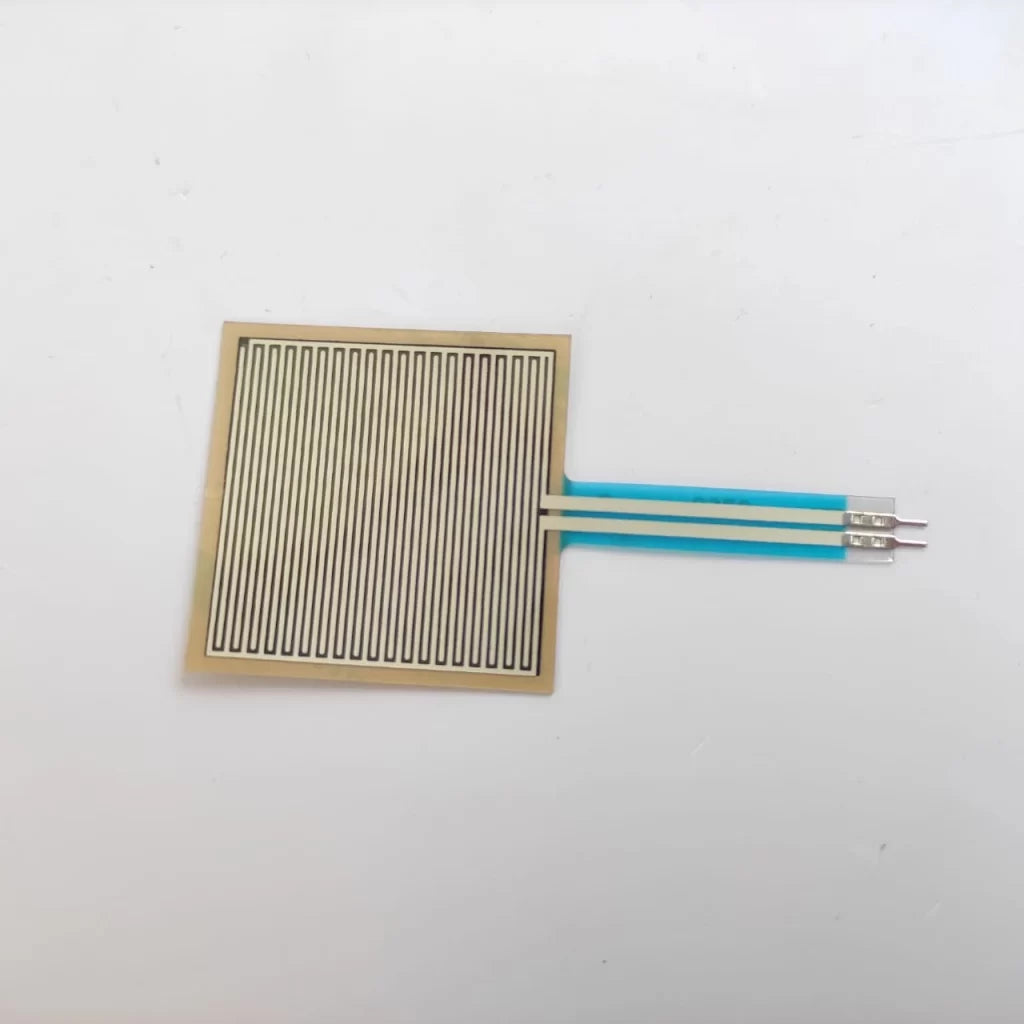
Force Sensor
Force Sensor
Couldn't load pickup availability
Share
Specification
- Actuation Force: 0.1 Newtons
- Force Sensitivity Range: 0.1 – 10.02 Newtons
- Non-Actuated Resistance: 10M W
- Device Rise Time: <3 microseconds
- Temp Operating Range: 30 – +70 ºC
- 16MHz Clock Speed
- 32 KB Flash Memory
- Dimensions:1.75×0.28 (inch)
- Sensing area: 0.3 (inch)
Description
Force sensors, also known as load cells, are devices designed to measure the force or load applied to them. They are commonly used in various industries and applications, including industrial automation, robotics, material testing, medical devices, and more.
Force sensors typically consist of a sensing element that converts the applied force into a measurable electrical signal. The sensing element can utilize different technologies, such as strain gauges, piezoelectric materials, or capacitive sensing.
These sensors are capable of measuring forces in various directions, including compression (pushing) and tension (pulling). They are designed to provide accurate and reliable force measurements within a specified range, often expressed in units like Newtons (N) or pounds (lb).
Force sensors come in a range of sizes and configurations to accommodate different force measurement requirements. They can be small and compact for applications with limited space, or larger and more robust for heavy-duty industrial applications.
The output of force sensors can be analog or digital, depending on the specific sensor model. Analog output is typically a voltage or current signal proportional to the applied force, while digital output can provide more precise and easily interpretable data.
These sensors find applications in various fields, such as weighing scales, force feedback in robotics, quality control in manufacturing processes, biomechanical research, and many more. They play a crucial role in accurately measuring and monitoring forces in a wide range of applications, contributing to improved efficiency, safety, and performance.